| Problem Based Learning:
|
|
Phyllis Leary Newbill, Tiffany A. Drape, Christine Schnittka, Liesl Baum, and Michael A. Evans
|
Problem-Based Learning is, as its name suggests, learning that occurs as a result of solving real-world problems (Combs, 2008). It is inherently meaningful and contextualized. Problem-based learning creates environments where students assume ownership of their learning; it is simply more interesting than memorizing information (Jonassen, Howland, Moore, & Marra, 2003). In this constructivist instructional method (Driscoll, 2005), the problem to be solved has “some social, cultural or intellectual value to someone” (Jonassen et al., 2003, p. 20). Savery (2006) defined problem-based learning in the classroom as having certain critical characteristics: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. Students have responsibility for their own learning. 2. Problems are ill-structured and allow for free inquiry. 3. Learning is interdisciplinary. 4. Collaboration is essential. 5. Self-directed learning informs group decisions. 6. Reflection is essential. 7. Self and peer assessment happens regularly. 8. Problems have real-world value. 9. Assessment checks process and product. (Savery, 2006, pp. 12–14)
Project based learning elements; (good summary of the key elements ) www.bie.org |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PBL— as opposed to
“projects”— relies on:
•rigorous
assessments
•challenging
questions
•proven
management methods
•exhibitions
of knowledge and skills to ensure powerful learning.
•Reports,
Presentations, Seminars
Markham, Thom. Project Based Learning Design and Coaching Guide . HeartIQ Press.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
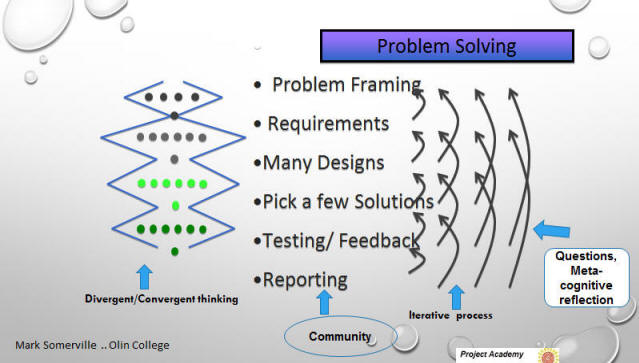
| PBL is not enough ... Students must be cognitively aware of skills they are using | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
In problem-based learning,
Beside solving the community, world, school problems,
“learning life skills along the way” is also a goal of the work.
Which Skills are we
going to focus on in this project? See pictorial example of this (PDF):
|